Yemen’s Houthi rebels vow open battle with Israel and the U.S., as fears rise of wider Mideast war

- Share via
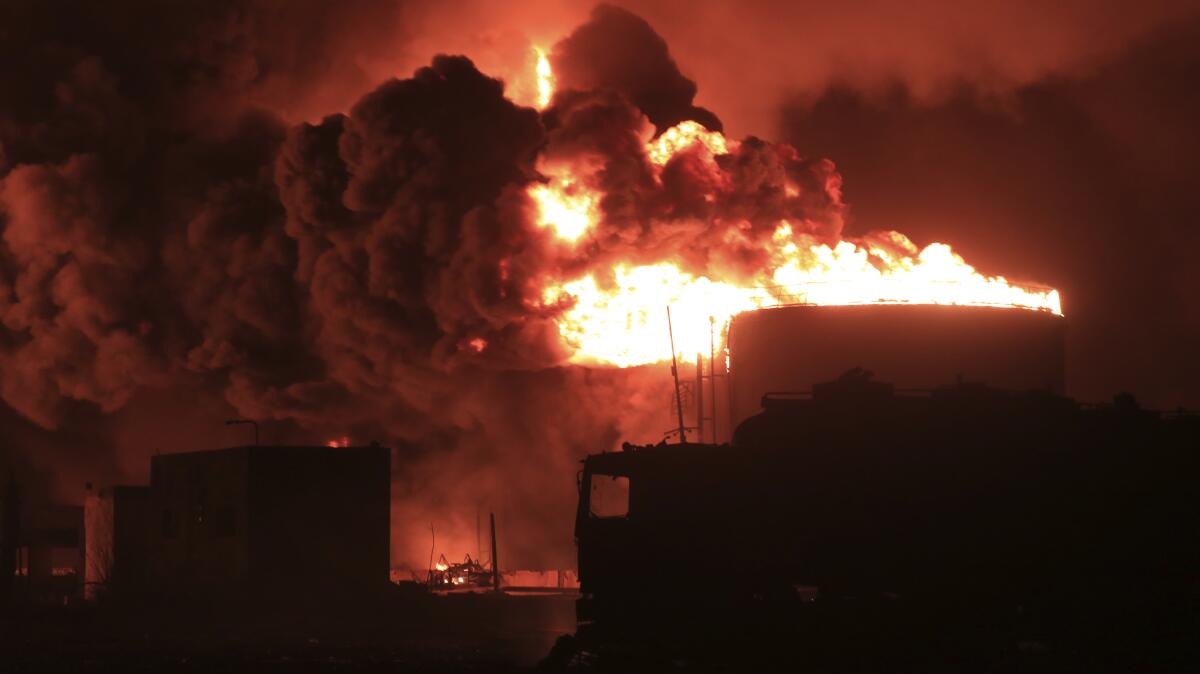
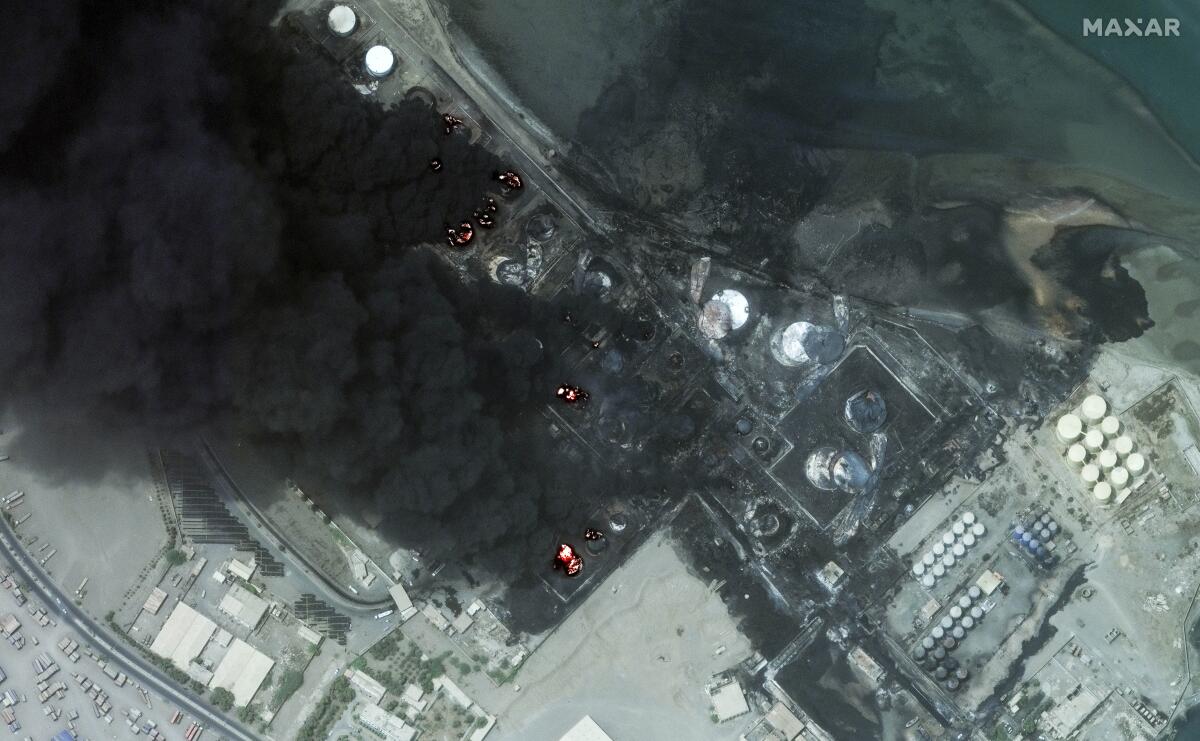
BEIRUT — After more than 1,000 miles and almost three hours of flight time, the squadron of Israeli F-15s and F-35s launched its missiles on Yemen’s Hudaydah port, leaving in its wake a raging blaze and renewed fears of a Middle East engulfed by wider war.
Israel’s retaliatory attack was meant as a fiery message to a militant group that hit Tel Aviv with a deadly drone strike the day before. But, experts say, Israel may have given the Houthi rebels the legitimacy they have long sought, leading them to escalate attacks on Israel and ships in the region.
Israel’s attack Saturday evening, which killed six dockworkers and injured dozens, was the country’s first strike on Yemeni territory. The drone strike from the Iran-backed Houthi militia, which controls wide swaths of Yemen and is allied with Hamas, managed to get through Israel’s defenses and kill one civilian and wound at least 10.
If anything, Israel’s strike is likely to further encourage the Houthis, said Hisham al Omeisy, a U.S.-based Yemeni analyst. It could play into their often-repeated narrative of championing Muslims against the United States and Israel.
“The Houthis desperately wanted this direct confrontation to legitimize their claim of being in a fight with Israel,” Al Omeisy said.
Christian areas scattered across Hezbollah-dominated southern Lebanon find themselves on the front line of a fight that few see as theirs.
The group — part of a regional network of Iran-backed factions operating in Lebanon, Yemen, Syria, Iraq and Gaza — has been lobbing missiles and drones at Israel (almost all of which have been intercepted). It is demanding Israel end the war in Gaza, which has killed more than 39,000 Palestinians in the territory, including civilians and combatants. The war began after Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7, killing about 1,200 people and taking some 250 hostage.
The Houthis have also repeatedly attacked ships transiting the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, including those with no links to Israel. The U.S. and Britain have launched multiple rounds of joint strikes on the Houthis over the shipping attacks.
Israel’s strikes on Yemen destroyed storage tanks with more than 150,000 tons of fuel, along with a number of cranes and piers, said Mohammed Albasha, a senior Yemen expert at the U.S.-based Navanti Group consulting firm.
Days later, fires still rage from the port, a crucial aid and fuel lifeline for Houthi-controlled areas of the country, where the majority of the country’s 33 million people live. Though firefighters have yet to fully put out the flames in the port’s fuel depot and power plant or clear debris from destroyed cranes, officials said Monday the port is operational.
Israel under fire for ‘GPS spoofing’ affecting airplane navigation systems in Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Egypt, Turkey and Cyprus.
In the hours after the strikes, Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant characterized the hit as a message not only to the Houthis but to Israel’s regional enemies.
“The fire that is currently burning in Hudaydah is seen across the Middle East and the significance is clear,” Gallant said after the Israeli strike.
“The Houthis attacked us over 200 times,” Gallant said. “The first time that they harmed an Israeli citizen, we struck them. And we will do this in any place where it may be required.”
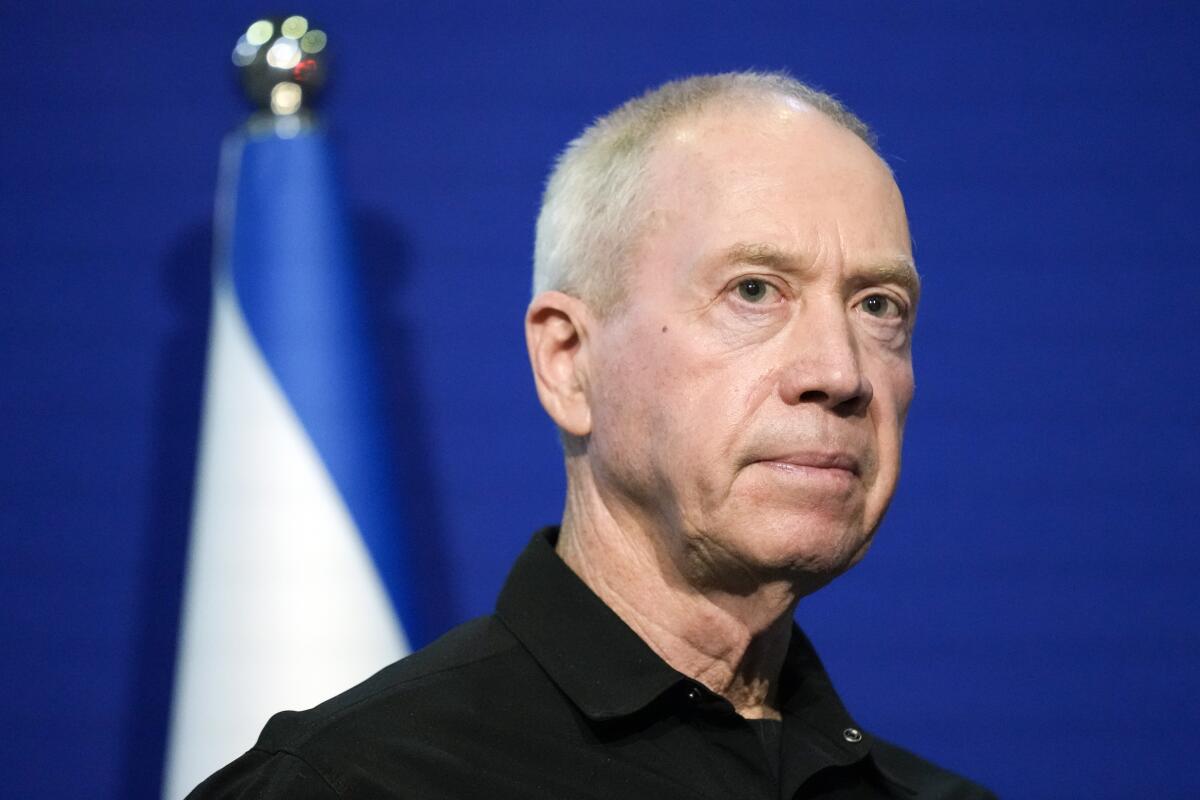

Yet it’s a message the Houthis are unlikely to heed, experts say.
“The Israeli attack was meant to shock and awe, but unfortunately you’re dealing with the Houthis,” said Al Omeisy.
The Houthis, who started out as anti-government rebels, had spent years battling the Yemeni state; in 2014 they overran the capital, Sana, then put their sights on the rest of the country. To stop them, a Saudi-led onslaught — bolstered by American weapons, intelligence and logistics support — launched a devastating air campaign and blockade that brought Yemenis to the brink of famine. By the time an April 2022 cease-fire was signed, the Houthis remained even stronger in the areas they controlled.
“Shock and awe and the use of overwhelming power didn’t really work on them when it was a coalition of countries hammering them,” Al Omeisy said. “So it won’t work now.”
Sometimes in Gaza it feels like a cigarette is the only thing that might help. But even that is out of reach.
Since the attack, Houthi officials have vowed a “huge” response to the Israeli strike, and on Sunday the group launched a ballistic missile on Israel that was intercepted. That same day, the group’s leader, Abdul Malik al-Houthi, gave a televised address in which he said he was “very happy” that the group was now engaged in a direct battle with Israel and the United States.
“The Israeli aggression against our country will contribute to a greater escalation of our operations against it and to the development of our capabilities as well, and the enemy will lose and incur more dangers upon itself,” he said.

The Lebanese Shiite group Hezbollah, the most powerful armed faction in Iran’s so-called axis of resistance, characterized Israel’s strike as a “foolish step” that “heralds a new and dangerous phase of extremely important confrontation at the level of the entire region.”
Israel has traded attacks with several groups in Iran’s axis, which also includes factions in Syria and Iraq, pushing the Middle East closer to an all-out war.
The expectation is that the Houthis, as well as their allies in other Iran-backed factions, will intensify their attacks both on Israel and in the Red Sea, utilizing more advanced Iranian-supplied weaponry than the group has possessed in the past, Albasha said.
“Historically, Iran didn’t give the Houthis the newest technology. Now they are,” he said. He pointed out that the drone used in the Tel Aviv attack, which the Houthis called Yafa (the Arabic name for Jaffa), was a modified version of the Houthi-manufactured Sammad 3 drone — but with a newer engine and possibly upgraded avionics.
Last week, the Houthis used drone boats to attack two vessels in the Red Sea. Reports said the drone boats were an upgraded design of the Toofan, a drone boat with a 4,500-pound payload capable of reaching 45 nautical miles per hour.

That any escalation would have consequences on Yemen, already the region’s poorest and one of its most war-ravaged nations, was not necessarily a problem for the Houthis, said Fatima Alasrar, a nonresident scholar at the Middle East Institute think tank.
“The Houthis have not shied away from leveraging conflict to expand their influence and capabilities,” she said.
“They will continue to strike irrespective of the consequences.”
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.














