A rhino got pregnant from an embryo transfer, a success that may help nearly extinct subspecies
- Share via
NAIROBI — Researchers say a rhinoceros was impregnated through embryo transfer in the first successful use of a method that might later make it possible to save the nearly extinct northern white rhino subspecies.
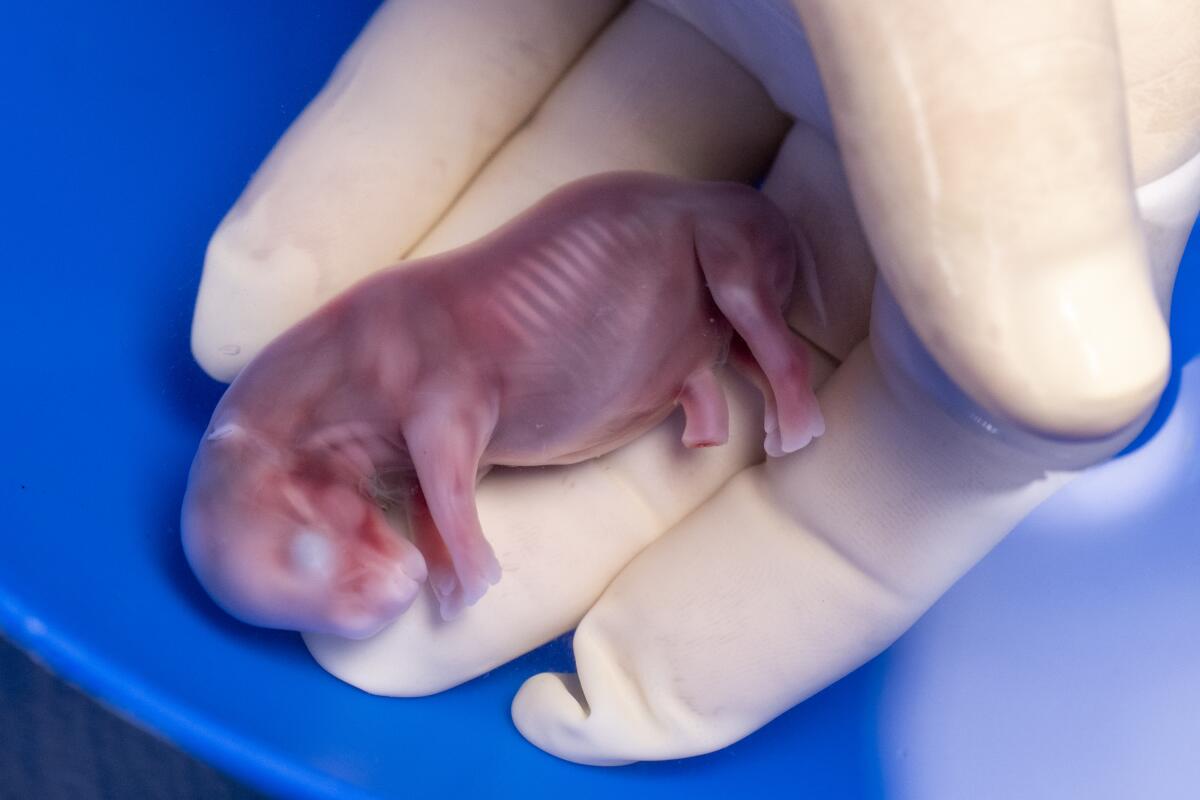
The experiment was conducted with the less endangered southern white rhino subspecies. Researchers created an embryo in a lab from an egg and sperm collected from rhinos and transferred into a southern white rhino surrogate at the Ol Pejeta Conservancy in Kenya.
“The successful embryo transfer and pregnancy are a proof of concept and allow [researchers] to now safely move to the transfer of northern white rhino em-bryos — a cornerstone in the mission to save the northern white rhino from extinction,” the group said in a statement.
However, the team learned of the pregnancy only after the surrogate rhino died of a bacterial infection in November. The rhino was infected when spores from the clostridium strain were released from the soil by floodwater, and the embryo was discovered during a postmortem examination.
Since the Endangered Species Act passed 50 years ago, more than 1,700 plants, mammals, fish, insects and more have been listed as threatened or endangered.
Still, scientists are very optimistic about their findings. “Now we have the clear evidence that an embryo that is frozen, thawed, produced in a test tube can produce new life and that is what we want for the northern white rhino,” Thomas Hildebrandt, the lead researcher and head of the Department of Reproduction at BioRescue, said in a statement.
Roughly 20,000 southern white rhinos remain in Africa. That subspecies as well as another species, the black rhino, are bouncing back from significant reduction in their populations because of poaching for their horns.
However, the northern white rhinoceros subspecies has only two known members in the world.
Najin, a 34-year-old, and her 23-year-old offspring, Fatu, are incapable of natural reproduction, according to the Ol Pejeta Conservancy, where they live.
The last male white rhino, Sudan, was 45 when he was euthanized in 2018 because of age-related complications. He was Najin’s sire.
Scientists stored his semen and that of four other dead rhinos, hoping to use them in in-vitro fertilization with eggs harvested from female northern white rhinos to produce embryos that eventually will be carried by southern white rhino surrogates.
Some conservation groups have argued that it is probably too late to save the northern white rhino with in vitro fertilization, as the species’ natural habitat in Chad, Sudan, Uganda, Congo and Central African Republic has been ravaged by human conflict.
Skeptics say the efforts should focus on other critically endangered species with a better chance at survival.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.











