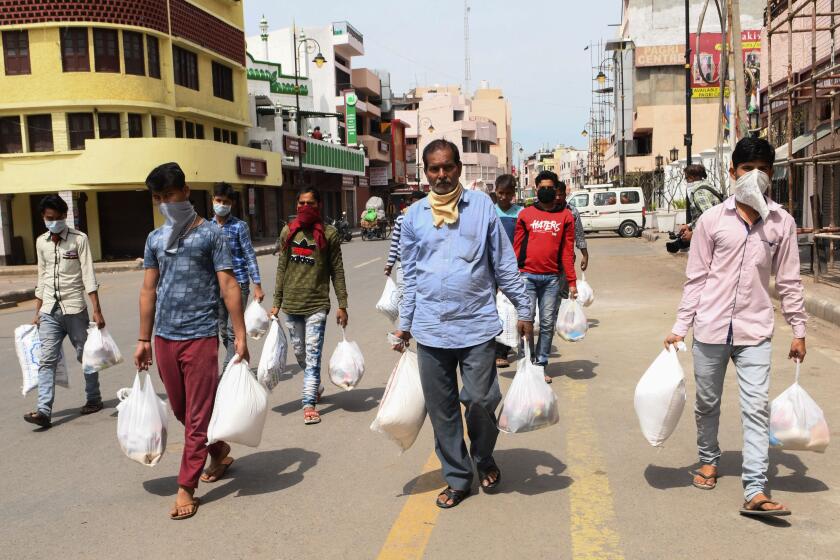
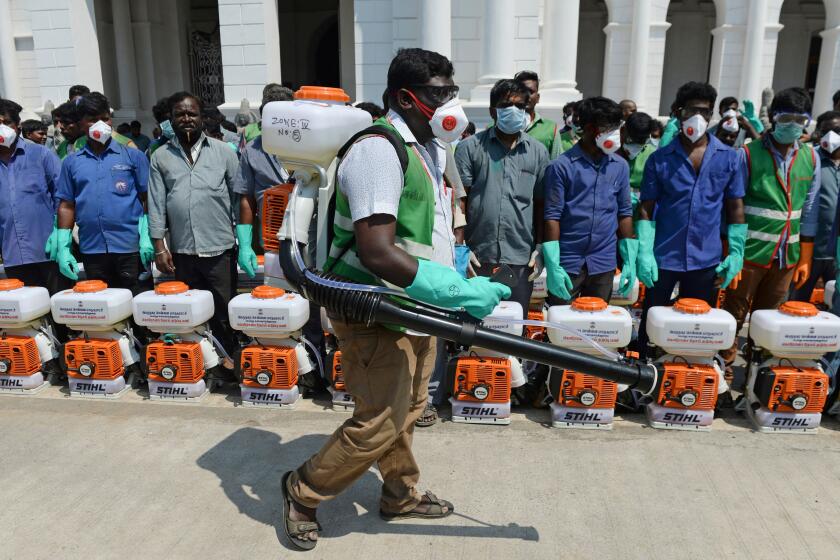
As coronavirus swamps India, hospitals turn away other sick people

- Share via
As cases of the coronavirus were rising steadily in India, 76-year-old Ravindra Nath Singh arrived at a private hospital in the northern city of Lucknow complaining of breathing trouble.
Already suffering from Parkinson’s disease, Singh was immediately admitted to intensive care March 20 and diagnosed with pneumonia. Doctors did not test him for the coronavirus because he had no travel history, but said he would need to remain hospitalized for at least a week, said his son, Jayant Singh.
But four days later, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced a nationwide lockdown “to save India” from the coronavirus and called on medical practitioners to halt nonessential surgeries in order to preserve hospital beds for the expected influx of COVID-19 patients.
The next morning, Jayant Singh was stunned when doctors told him his father — who was still in the ICU, hooked up to a catheter and feeding tube — was well enough to be discharged and could be cared for at home.
“Everything changed after the lockdown speech,” said Singh, 42, a data scientist who works with the pharmaceutical industry.
In the United States, doctors have begun to prepare for life-and-death decisions over how to allocate hospital beds, ventilators and other equipment amid a surge in COVID-19 cases. In India — a country of 1.3 billion people that spends only a fraction of what other major economies do on doctors and healthcare — the rationing of medical care has already begun.

Patients suffering from chronic diseases, including those with HIV and cancer, and older Indians such as Ravindra Nath Singh, are particularly vulnerable as the country deals with a cascading outbreak of the coronavirus, which by Monday had infected more than 4,700 Indians — a fourfold increase in a little more than a week.
Although Modi did not explicitly order rationing of care, Jayant Singh said in an interview that he tried to have his ailing father admitted at three other hospitals in Lucknow but was turned away each time. At one hospital, he was told that patients older than 70 “are not to be admitted, to make beds available for younger patients.”
A spokesperson for Ajanta Hospital, where Singh was treated, denied forcibly discharging him and said his family wanted to take him home.
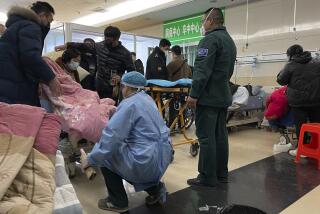
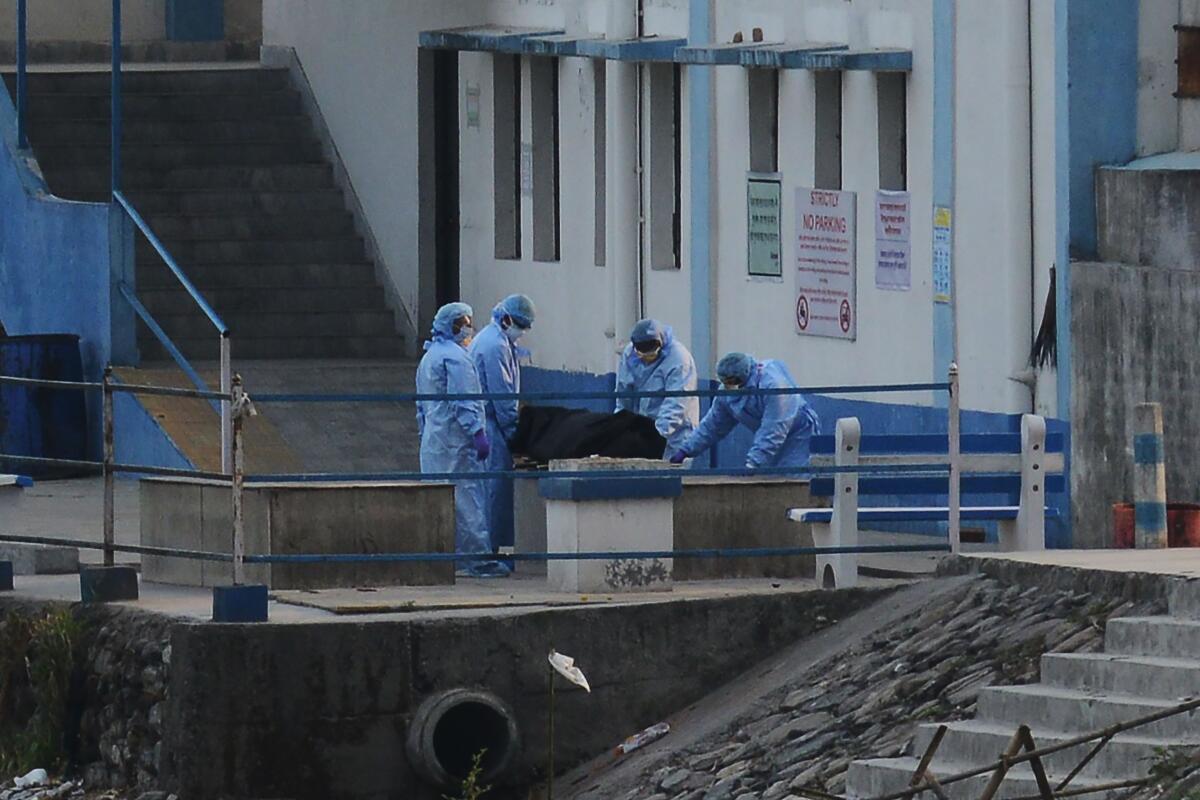
Across India, many hospitals have closed their outpatient departments because of an expected influx of coronavirus patients or because medical staff began to show symptoms of the disease, which had killed at least 118 Indians as of Monday, according to official figures. (Experts say the true scale of India’s coronavirus outbreak is unknown, because the country has one of the world’s lowest rates of testing.)
In announcing the lockdown, which is due to be lifted April 14, Modi gave Indians just four hours’ notice, bringing an abrupt halt to regular, time-sensitive medical services such as drug deliveries, immunizations, outpatient care and follow-up visits for tuberculosis and cancer patients.
The government of Rajasthan state suspended children’s vaccinations and prenatal checkups. Hospitals in the city of Chandigarh converted psychiatric wards into COVID-19 isolation facilities. The All India Institute of Medical Sciences, the country’s premier medical facility, indefinitely postponed non-COVID-19 appointments and stopped admitting new cancer patients.
The stoppage of routine care shows how the sudden onslaught of the virus has overwhelmed health systems around the world.
“We have a trade-off,” said Ramanan Laxminarayan, director of the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy in Washington. “If we don’t contain COVID-19, we risk losing healthcare workers to the disease, which could then result in long-term consequences for health.…There are no easy answers.”
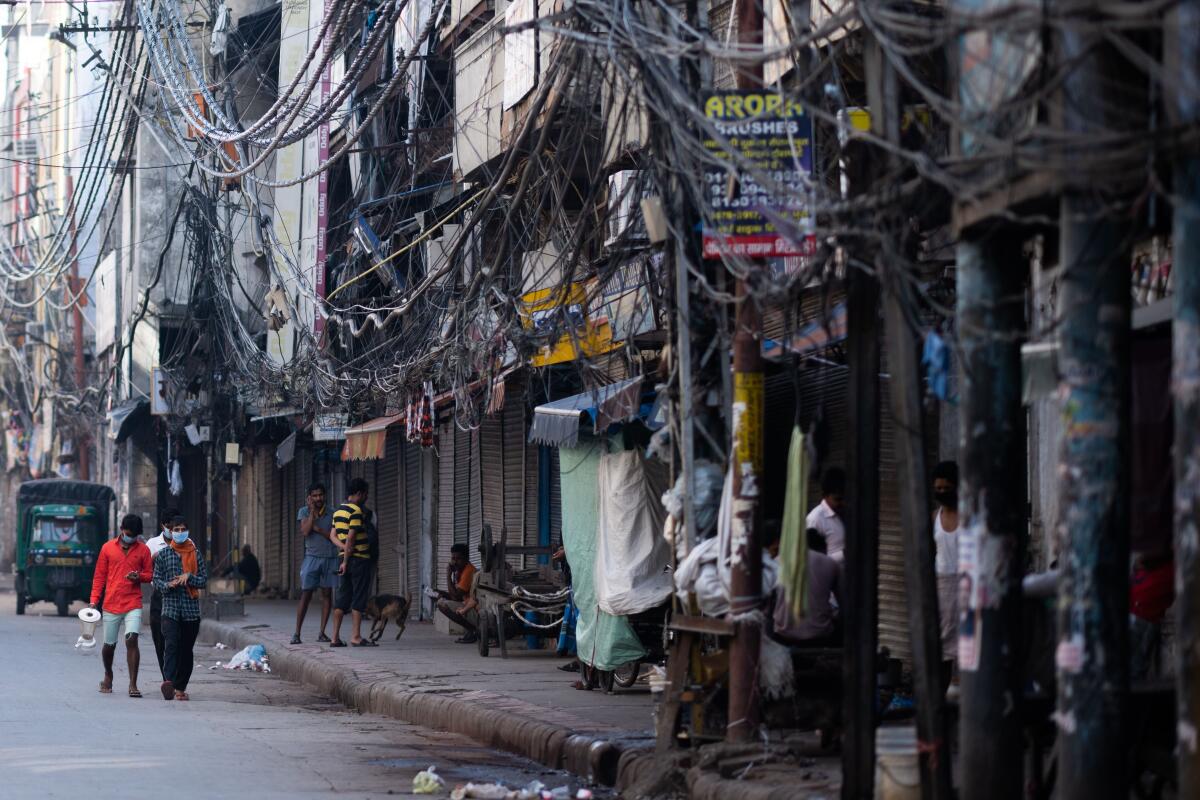

Even before the increase in COVID-19 cases, India’s emergency rooms were full, and at government hospitals — the only ones sanctioned to treat the coronavirus — medical staffers were working beyond their capacity. India has just one government doctor for every 10,000 people, compared with the internationally recommended ratio of 1 to 1,000.
One group of patients has emerged as a particular concern for health experts: India’s 2.8 million tuberculosis sufferers, the most of any country. TB is the world’s deadliest infectious disease, and World Health Organization guidelines require patients to visit clinics daily to ingest medication in the presence of a health worker.
The WHO has advised health professionals to provide TB patients with a sufficient supply of drugs and to use digital tools to stay in touch with them during lockdowns. But many patients appear to lack reliable access to medication, particularly to ameliorate the often-debilitating side effects caused by the drugs most often used to treat TB in India.
A three-week lockdown affecting 1.3 billion people has unleashed chaos as stranded migrant workers sleep in streets and police beat curfew-breakers.
Saurabh Rane, a TB survivor and activist, said he had heard from several patients across India who were worried about access to drugs during the coronavirus pandemic.
“One patient has been asked by her doctors to continue taking medicines that have serious side effects and turn up at the emergency room if things go bad — as they invariably do with TB care,” Rane said.

In Bihar, one of India’s poorest states, TB patients were provided with a month’s supply of drugs. But health workers said that people who had come in with mouth ulcers and other symptoms of TB but were yet to be diagnosed would probably go without care for several more weeks.
Dr. Zarir Udwadia, India’s leading pulmonologist, said he had been using telemedicine “to try and bridge the gap” with his patients, many of whom suffer from multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, a particularly lethal strain of the disease.
An oncologist in the eastern city of Chennai said he hears from about 10 leukemia patients every day who haven’t been able to get medication because of India’s travel restrictions.

One of his patients — a 36-year-old diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukemia, a type of cancer that starts in the bone marrow — said in an interview that she had gone nearly two weeks without medication. Living in a rural district 250 miles from Chennai, she has to travel by bus to the clinic once a month to collect the drugs. But bus services have been suspended, and couriers who could deliver the medication are banned from working as well.
“I am concerned many patients with cancer will relapse due to inadequate care,” said the oncologist, who requested anonymity to protect his job at a government hospital.
Experts question India’s coronavirus preparedness in light of its crowds, weak public health system and prevalence of other respiratory illnesses.
The coronavirus threatens to overwhelm India’s medical system as dozens of health workers test positive for the virus every day and doctors walk off the job because of a lack of masks, gloves and other protective gear.
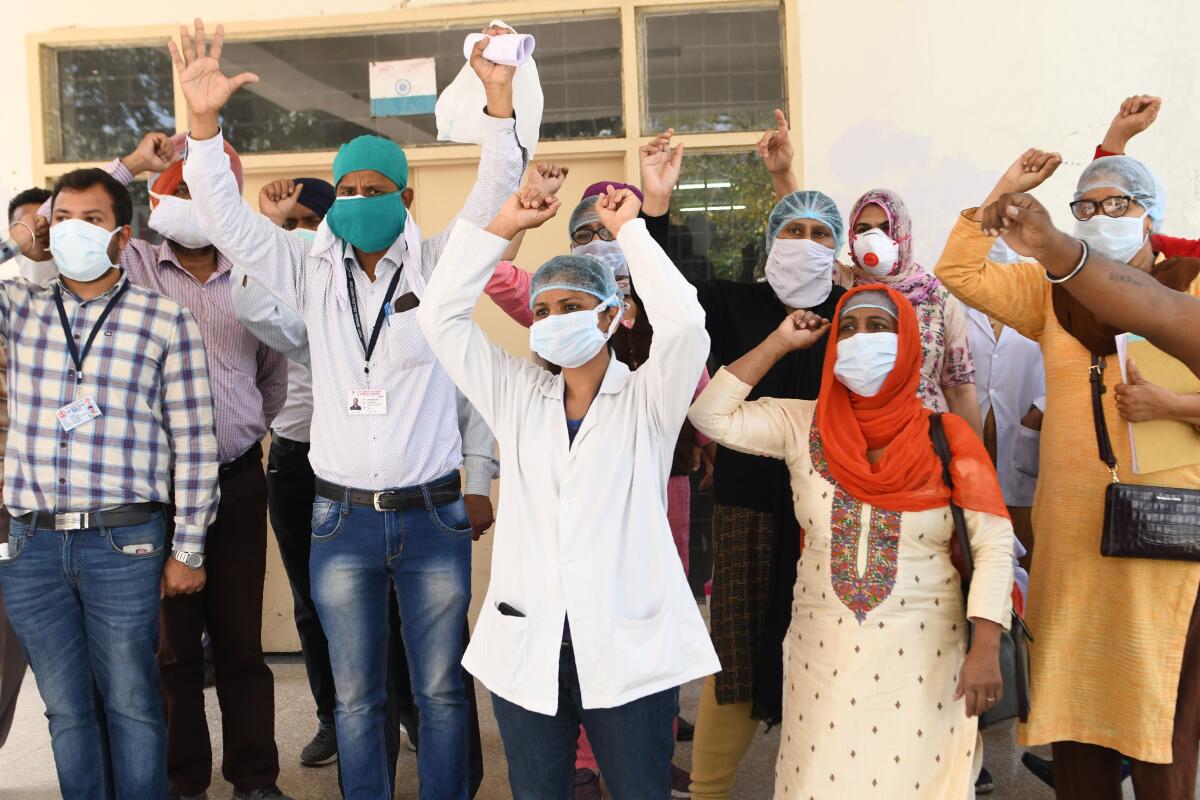

Last week, the New Delhi regional government refused to accept the resignations of doctors and nurses who had complained of insufficient equipment. In the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, about 4,700 ambulance drivers went on strike last month over a lack of safety gear and health insurance, returning to work the next day only after a panicked state government promised that their demands would be met.
The emphasis on the coronavirus has frustrated many families like the Singhs in Lucknow. After Ravindra Nath Singh was discharged from the hospital last month, a doctor in their Lucknow neighborhood reinserted his feeding tube and catheter at home.
“They should not discontinue treating other illnesses,” Jayant Singh said. “We may save people from COVID-19 but allow others to die from medical negligence by withholding other, equally important and life-saving care.”
For several days, as he watched his father fight to recover at home, “I was praying he dies, just so his suffering could end,” Singh said. His condition is stable, for now.
Times staff writer Bengali reported from Singapore and special correspondent Krishnan reported from Goa, India.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.