Experts question WHO’s ability to lead probe into the pandemic’s origins
- Share via
BEIJING — As the World Health Organization draws up plans for the next phase of its inquiry into how the COVID-19 pandemic started, an increasing number of scientists say the U.N. agency isn’t up to the task and shouldn’t be the one to investigate.
Numerous experts, some with strong ties to WHO, say that political tensions between the U.S. and China make it impossible for an investigation by the agency to find credible answers.
They say what’s needed is a broad, independent analysis closer to what happened after the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster.
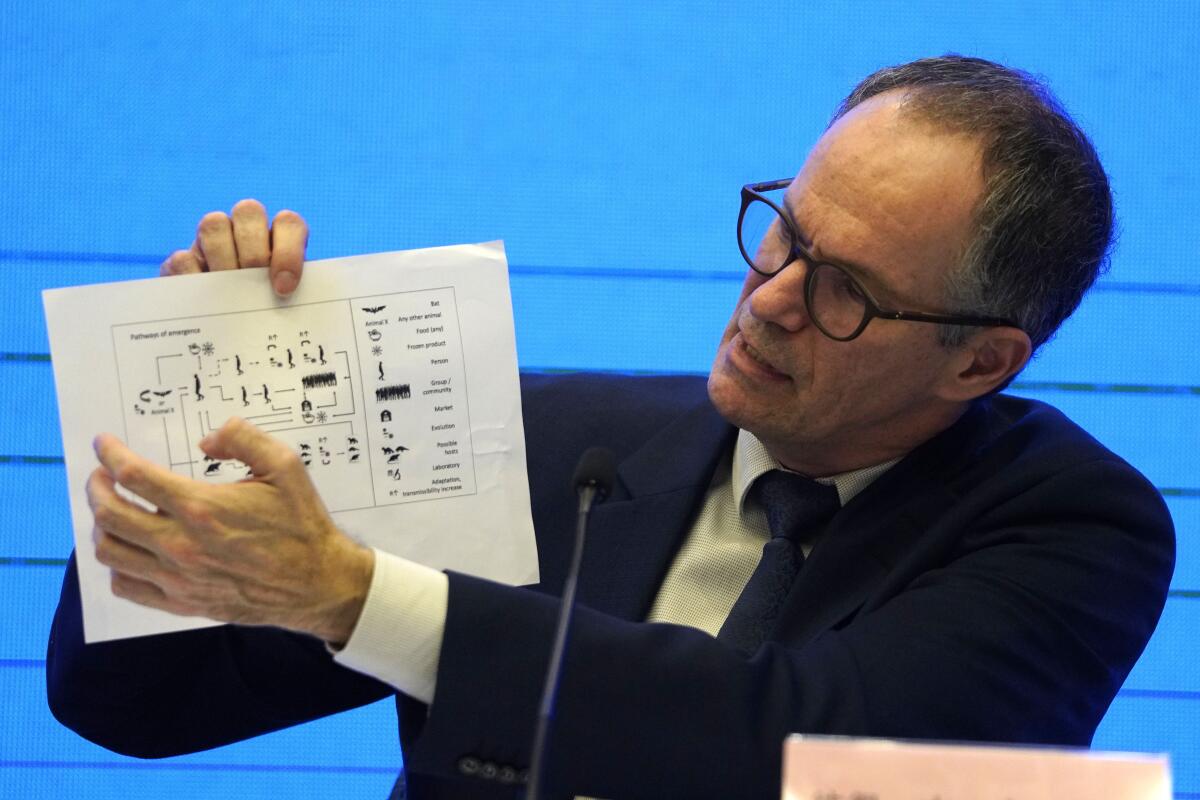
The first part of a joint WHO-China study of how COVID-19 started concluded in March that the virus probably jumped to humans from animals and that a lab leak was “extremely unlikely.” The next phase might try to examine the first human cases in more detail or pinpoint the animals responsible — possibly bats, perhaps by way of some intermediate creature.
But the idea that the pandemic somehow started in a laboratory — and perhaps involved an engineered virus — has gained traction recently, with President Biden in May ordering a review of U.S. intelligence within 90 days to assess the possibility.
WHO’s emergencies chief, Dr. Michael Ryan, said recently that the agency was working out the final details of the next phase of its investigation and that because WHO works “by persuasion,” it lacks the power to compel China to cooperate.
Some said that is precisely why a WHO-led examination is doomed to fail.
“We will never find the origins relying on the World Health Organization,” said Lawrence Gostin, director of the WHO Collaborating Center on Public Health Law and Human Rights at Georgetown University. “For a year and a half, they have been stonewalled by China, and it’s very clear they won’t get to the bottom of it.”
Gostin said the U.S. and other countries can try to piece together what intelligence they have, revise international health laws to give WHO the powers it needs, or create some new entity to investigate.
Understanding the origins of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is a linchpin for future pandemic prevention.
The first phase of WHO’s mission required getting China’s approval not only for the experts who traveled there but for their entire agenda and the report they ultimately produced.
Richard Ebright, a molecular biologist at Rutgers University, called it a “farce” and said that determining whether the virus jumped from animals or escaped from a lab is more than a scientific question and has political dimensions beyond WHO’s expertise.
The closest genetic relative to the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 was previously discovered in a 2012 outbreak, after six miners fell sick with pneumonia after being exposed to infected bats in China’s Mojiang mine. In the last year, however, Chinese authorities sealed off the mine and confiscated samples from scientists while ordering locals not to talk to visiting journalists.
Although China initially pushed hard to look for the coronavirus’ origins, it pulled back abruptly in early 2020 as the virus overtook the globe. An Associated Press investigation in December found Beijing imposed restrictions on the publication of COVID-19 research, including mandatory review by central government officials.
Scientists are urging their colleagues to dig deeper into the origins of the coronavirus behind the pandemic, including the possibility of a lab escape.
Jamie Metzl, who sits on a WHO advisory group, has suggested along with colleagues the possibility of an alternative investigation set up by the Group of 7 industrialized nations.
Jeffrey Sachs, a professor at Columbia University, said the U.S. must be willing to subject its own scientists to a rigorous examination and recognize that they might be just as culpable as China.
“The U.S. was deeply involved in research at the laboratories in Wuhan,” Sachs said, referring to U.S. funding of controversial experiments and the search for animal viruses capable of triggering outbreaks.
“The idea that China was behaving badly is already the wrong premise for this investigation to start,” he said. “If lab work was somehow responsible [for the pandemic], the likelihood that it was both the U.S. and China working together on a scientific initiative is very high.”
Cheng reported from London.








