NASA spacecraft begins 2-year trip home with asteroid rubble

- Share via
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — With rubble from an asteroid tucked inside, a NASA spacecraft fired its engines and began the long journey back to Earth on Monday, leaving the ancient space rock in its rearview mirror.
The trip home for OSIRIS-REx, the robotic prospector, will take two years.
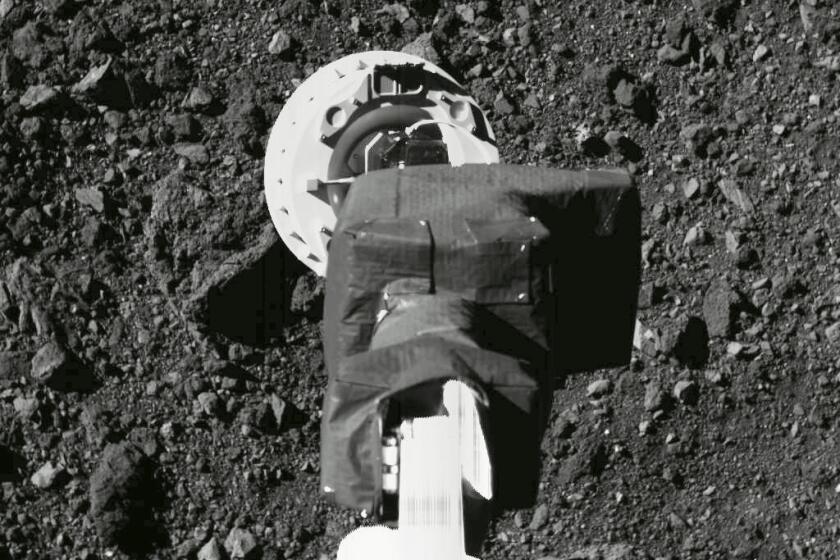
OSIRIS-REx reached asteroid Bennu in 2018 and spent two years flying near and around it, before collecting rubble from the surface last fall.
Dante Lauretta, the mission’s principal scientist based at the University of Arizona, estimates the spacecraft holds between one-half and a full pound of mostly bite-size chunks. Either way, it easily exceeds the target of at least 2 ounces.
It will be the biggest cosmic haul for the U.S. since the Apollo mission retrieved moon rocks. While NASA has returned comet dust and solar wind samples, this is the first time it’s gone after pieces of an asteroid. Japan has accomplished it twice, but in tiny amounts.
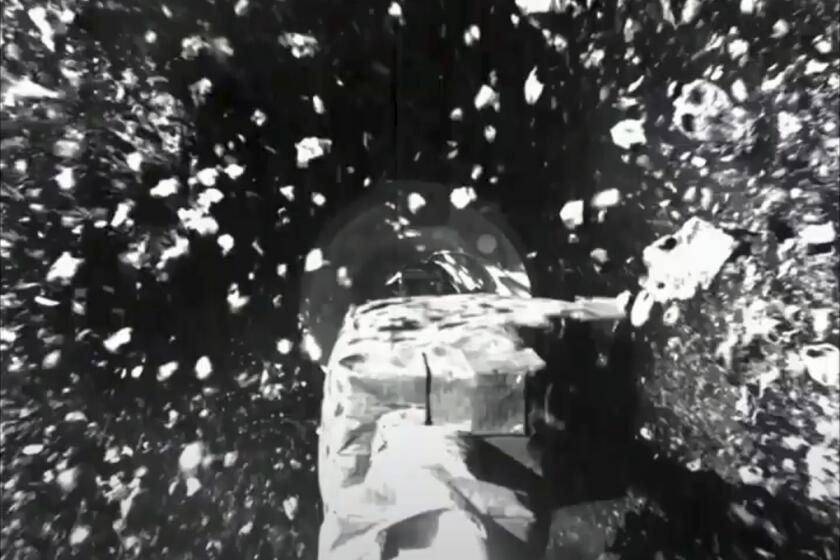
A NASA spacecraft descended to an asteroid Tuesday and momentarily touched the surface to collect a handful of cosmic rubble that will be brought to Earth.
Scientists described Monday’s departure from Bennu’s neighborhood as bittersweet.
“I’ve been working on getting a sample back from an asteroid since my daughter was in diapers and now she’s graduating from high school, so it’s been a long journey,” said NASA project scientist Jason Dworkin.
Added Lauretta: “We have gotten used to being at Bennu and seeing new and exciting images and data coming back to us here on Earth.”
OSIRIS-REx was already nearly 200 miles from the solar-orbiting Bennu when it fired its main engines Monday afternoon for a fast, clean get-away.
Colorado-based flight controllers for spacecraft builder Lockheed Martin applauded when confirmation arrived of the spacecraft’s departure: “We’re bringing the samples home!”
Scientists hope to uncover some of the solar system’s secrets from the samples vacuumed last October from Bennu’s dark, rough, carbon-rich surface. The asteroid is an estimated 1,600 feet wide and 4.5 billion years old.
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft crushed rocks and sent rubble flying as it briefly touched an asteroid, a strong indication that it had succeeded in collecting samples.
Bennu — considered a broken chunk from a bigger asteroid — is believed to hold the preserved building blocks of the solar system. The returning pieces could shed light on how the planets formed and how life arose on Earth. They also could improve Earth’s odds against any incoming rocks.
Although the asteroid is 178 million miles away, OSIRIS-REx will put another 1.4 billion miles on its odometer to catch up with Earth.
The SUV-size spacecraft will circle the sun twice before delivering its small sample capsule to Utah’s desert floor on Sept. 24, 2023. That will end the more than $800-million mission, which launched from Cape Canaveral in 2016.
The precious samples will be housed at a new lab under construction at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. The Houston facility is already home to hundreds of pounds of lunar material collected by the 12 Apollo moonwalkers from 1969-72.
Scientists initially thought the spacecraft had stored 2 pounds of asteroid rubble, but then revised their estimate downward. They won’t know for certain how much is on board until the capsule is opened after touchdown.
“Every bit of sample is valuable,” Dworkin said. “We have to be patient.”
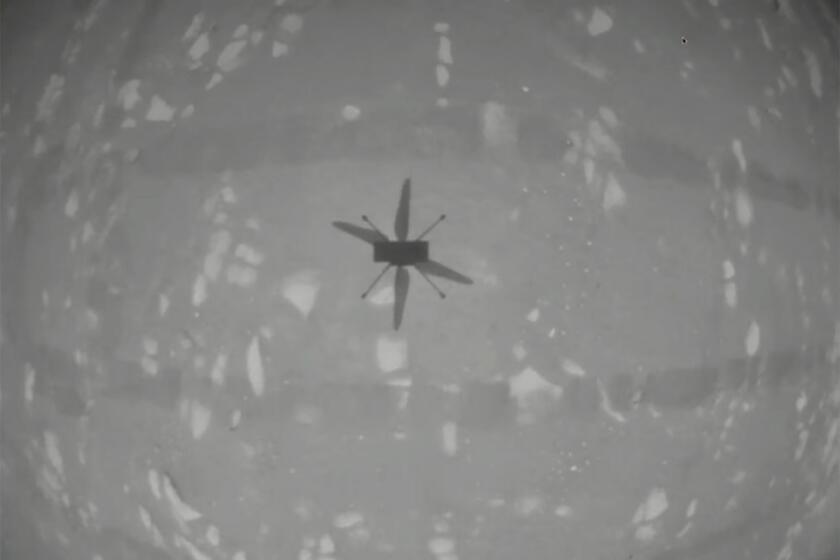
NASA’s experimental Mars helicopter rises from the dusty red surface into the planet’s thin air, achieving the first powered flight on another planet.
NASA has more asteroid projects planned.
Set to launch in October, a spacecraft named Lucy will fly past swarms of asteroids out near Jupiter, while a spacecraft known as Dart will blast off in November in an attempt to redirect an asteroid as part of a planetary protection test. Then in 2022, the Psyche spacecraft will take off for an odd, metallic asteroid bearing the same name.
None of these missions, however, involve sample return.