- Share via
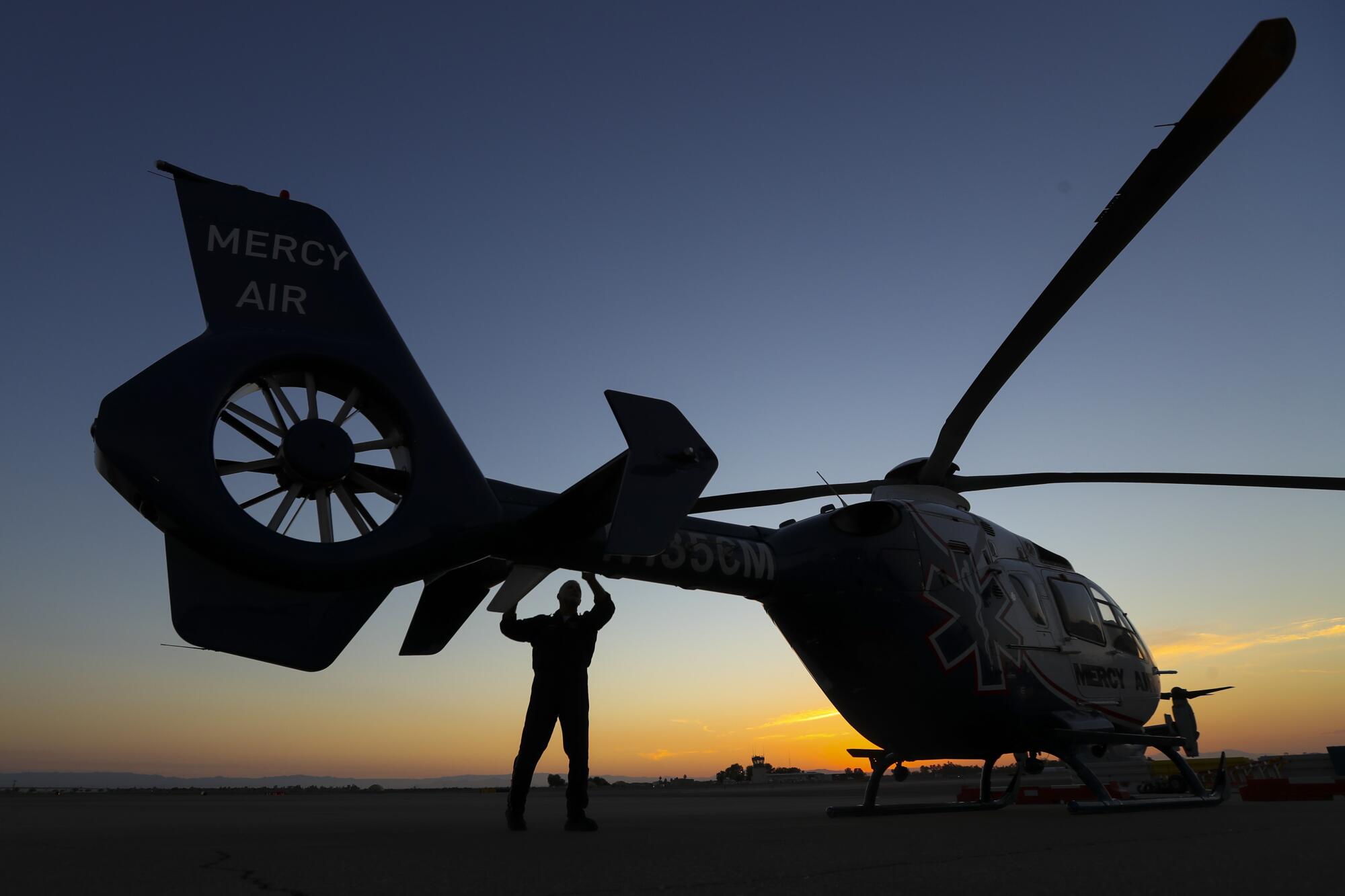
The medical flight crew of Mercy Air was getting ready for bed when they got their first call of the day. A stroke patient had to be transported from El Centro Regional Medical Center to UC San Diego Medical Center in Hillcrest.
Michael Bobeck, an army vet and pilot on duty, began a routine assessment of the flight risks. The twin-engine helicopter had enough fuel for the 174-mile round trip. Oxygen tanks were full. Fog was expected to move over San Diego County but not for another four to five hours.
“The risk was low to low medium,” he said. “So we decided to go for it.”
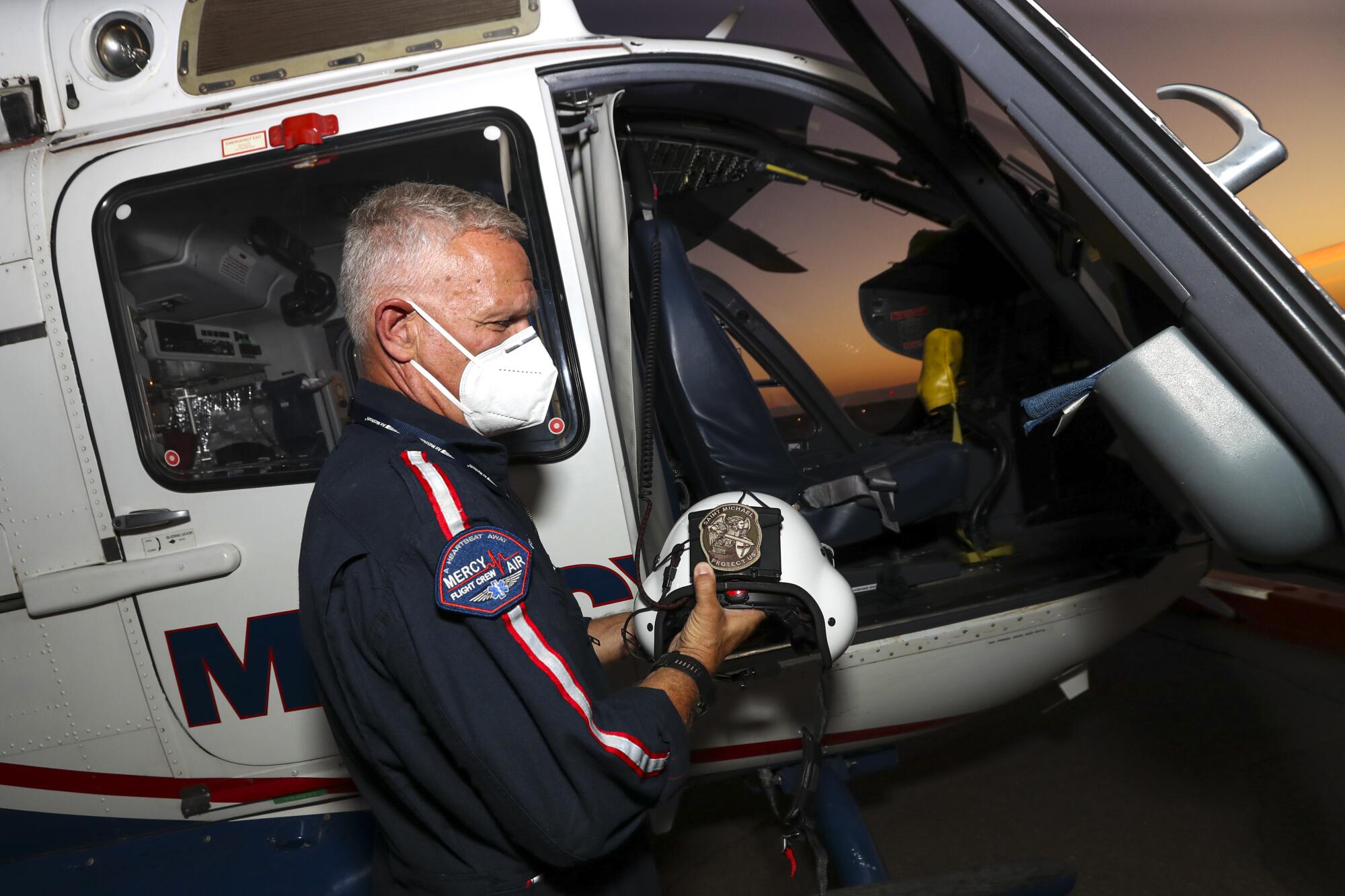

Less than 13 minutes after taking the call Sunday night, Bobeck and the flight crew — a nurse and paramedic — flew 10 miles south from the Mercy Air base at Imperial County Airport to El Centro.
Up until then, it had been an unusually quiet day for the crew. Even the call was a break from months of transporting COVID-19 patients out of Imperial County, a rural and impoverished region with a largely Latino population of about 180,000 people that has become a hotspot for the disease.
The county has been averaging 900 infections per 100,000 people in the last two weeks, compared with L.A. County’s 371. The county also has the highest mortality rate in the state, averaging 28 deaths per 100,000 people. The rate in Los Angeles County is just over five deaths per 100,000 people; in California as a whole it is almost 19 per 100,000.
County health officials link the increase of infection rates to May when the large industrial Mexican border city of Mexicali stopped receiving COVID-19 patients, forcing U.S. citizens living there to cross the border into Imperial County and seek care.

The county’s two hospitals — El Centro Regional Medical Center and Pioneers Memorial Healthcare District — were already dealing with an influx of COVID-19 patients that officials say was due to recent holiday gatherings.
On May 19, Dr. Adolphe Edward, chief executive of El Centro Regional Medical Center, said his hospital would stop receiving COVID-19 patients.
“Our numbers skyrocketed overnight,” he said. “We want to make sure we don’t overwhelm either one of the hospitals or the system with COVID-19 patients to the point that we can’t take care of you.”
Soon afterward, hospitals began stabilizing COVID-19 patients and moving them out of Imperial County. State officials said at least 500 COVID-19 patients were taken to hospitals outside the county.
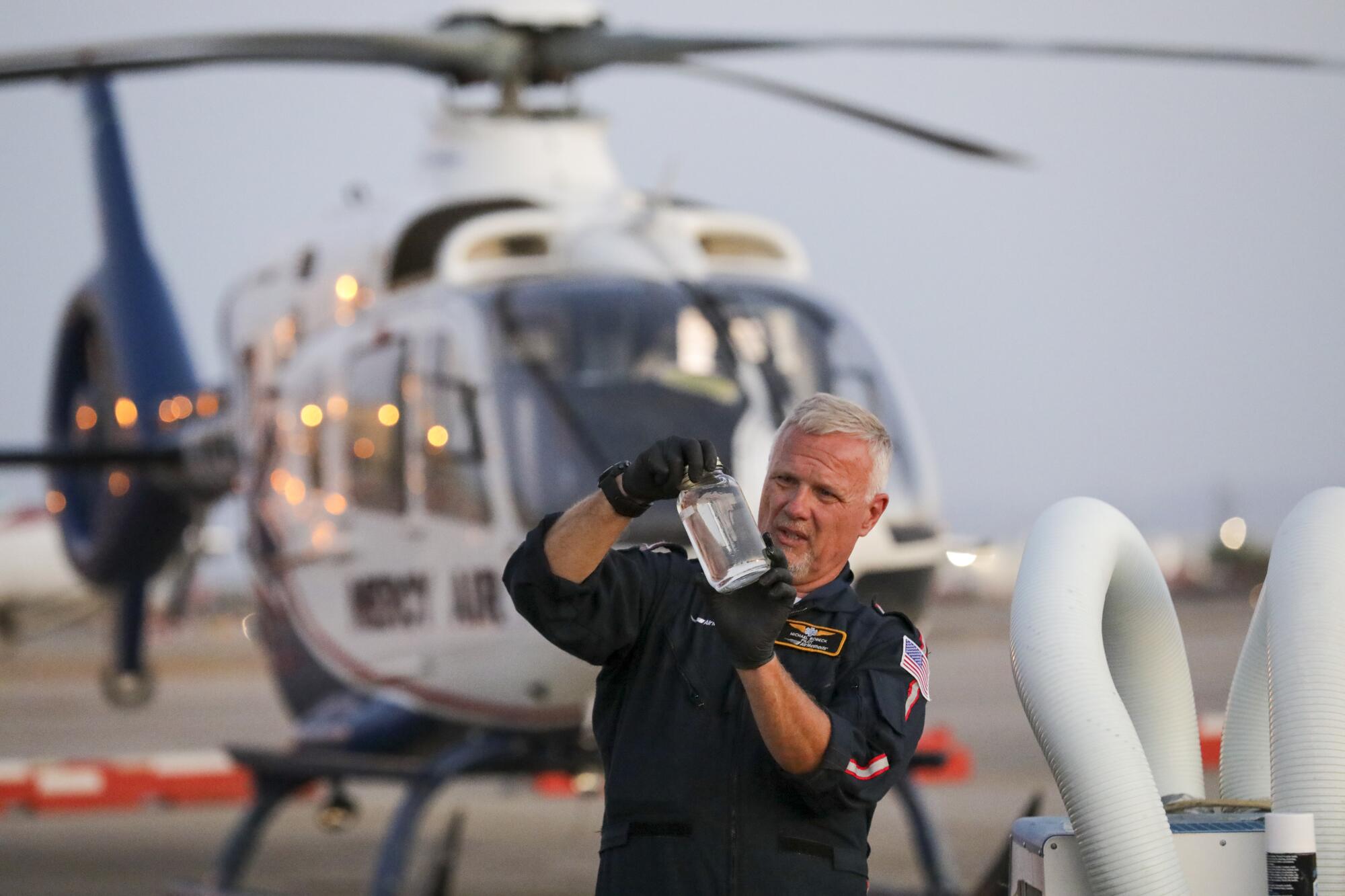

Answering the call that month was Mercy Air, one of two air medical companies serving the area.
The company is owned and operated by Air Methods, one of the largest air medical transport companies in the U.S. It operates 300 bases in 48 states, many of them located in California and Nevada.
For more than two decades, Mercy Air was providing service to Imperial County from its bases in San Diego and Riverside County. But two years ago, it decided to set up a base at Imperial County Airport.
“One of our objectives, our focus is to bring our services to underserved communities where there’s a big distance between the patient and the level of care they need,” Bill Hinton, area manager for Mercy Air and Air Methods, said. “You’ve heard of the ‘golden hour?’ You know, if somebody is in a car accident that first hour is the most important time frame.”
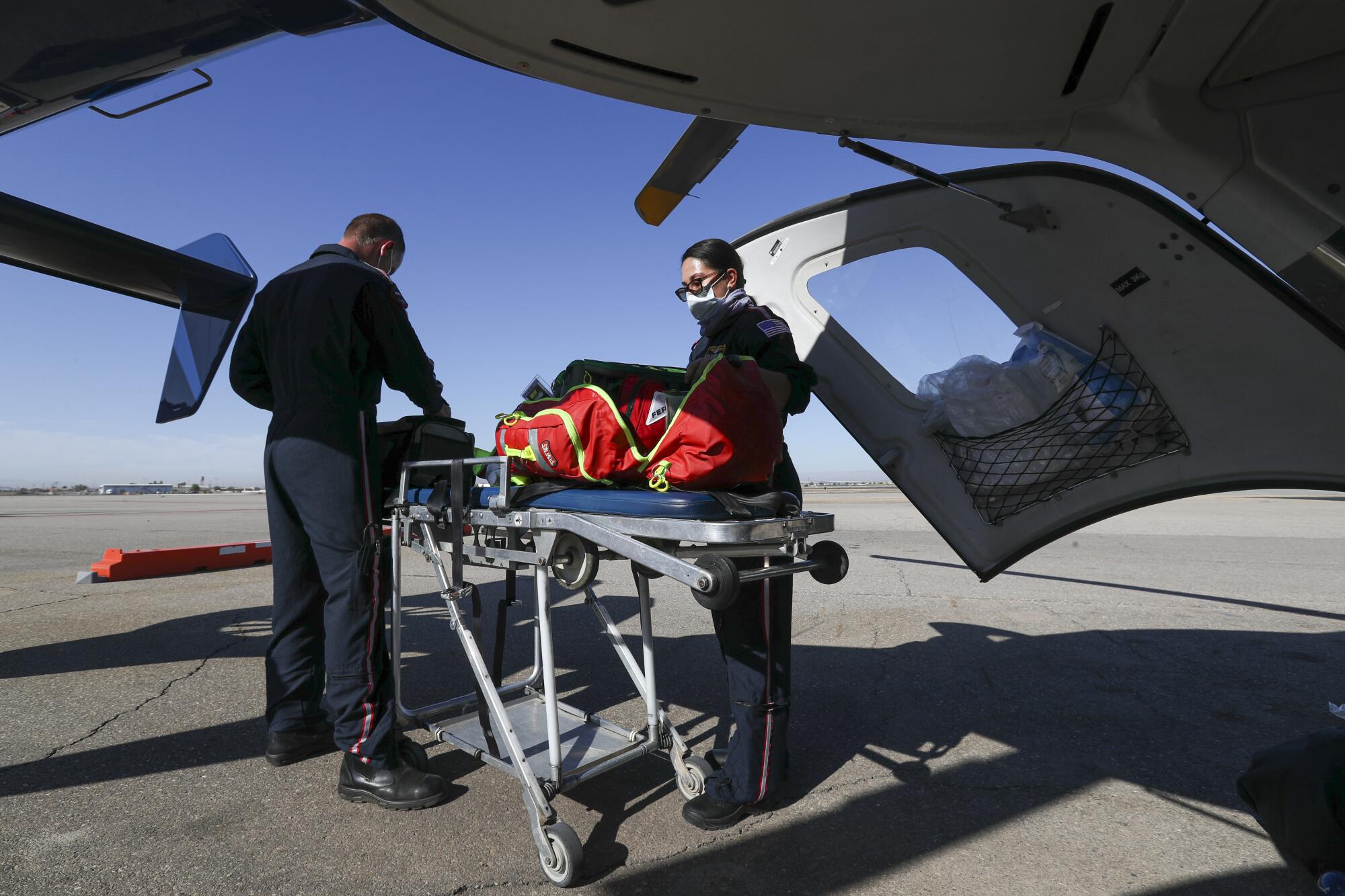

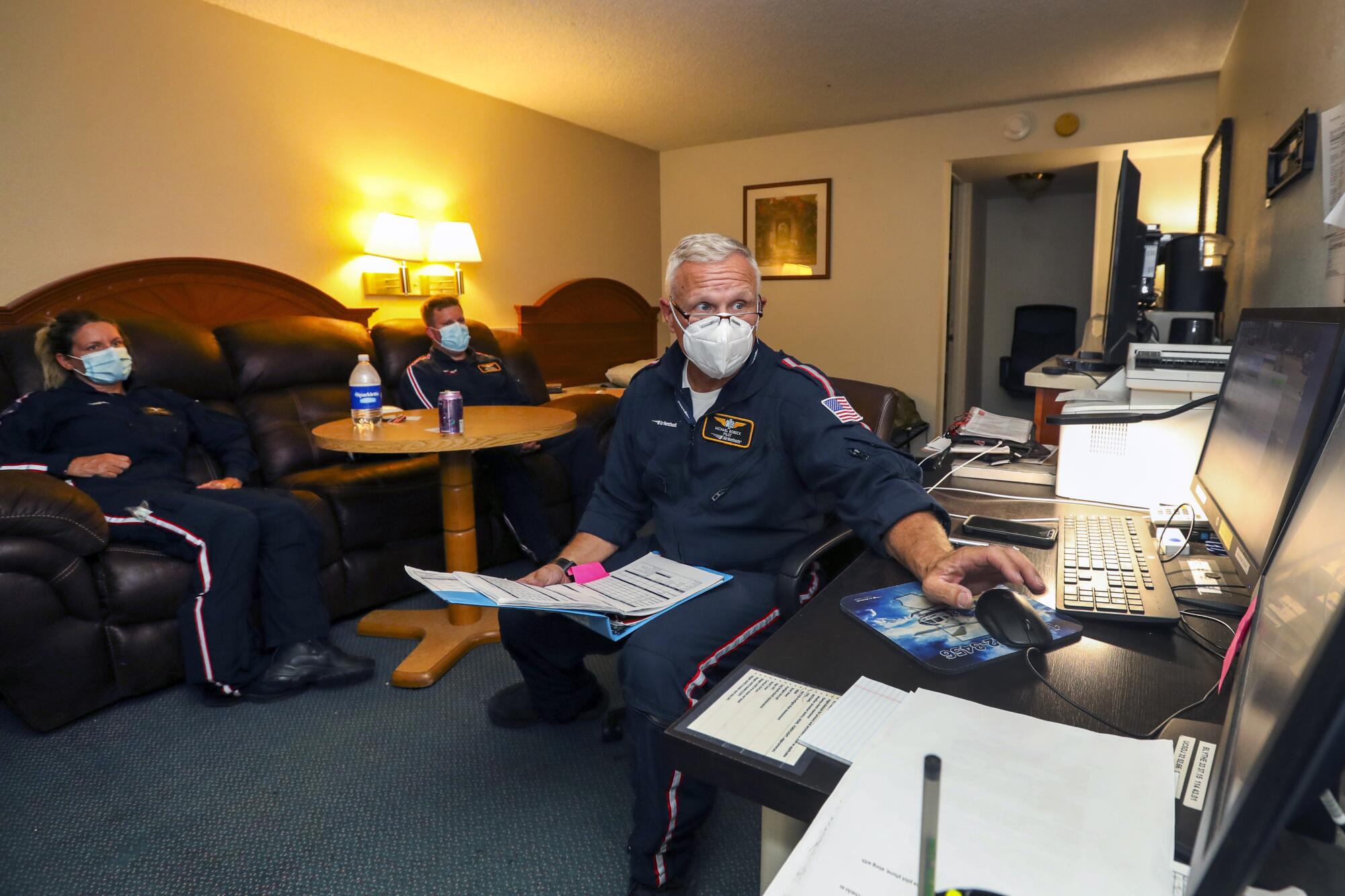
Mercy Air was working on completing construction of a new base at the airport when the pandemic brought everything to a halt. For now, the teams of pilots, critical care nurses and paramedics have been working out of a hotel about 300 feet from the airport.
Hinton said aircraft from the surrounding bases have been brought in to help deal with the high volume of transport requests by the two hospitals in Imperial County.
Medic teams with Mercy Air typically respond to car accidents and other emergencies near the border, state parks and the Imperial Sand Dunes, a popular site for off-roading enthusiasts. They get steady work from patients who need to receive advance care from hospitals elsewhere, such as in San Diego.
“Then COVID-19 hit,” Hinton said.

Derek Hughes, a paramedic for Mercy Air, said average patient transports were at least two a day. But that slowly began to go up, and by spring it had doubled.
Hinton said finding beds in nearby hospitals started to become increasingly difficult.
“We started seeing transports go out to Riverside, Las Vegas and Phoenix,” he said. “The farthest north we’ve gone by helicopter was Santa Barbara.”
“They’ve been all over the place right now, even to hospitals we’ve never transported patients to before,” he added.
Mercy Air officials say since March they have taken nearly 100 Covid-19 patients out of Imperial County.
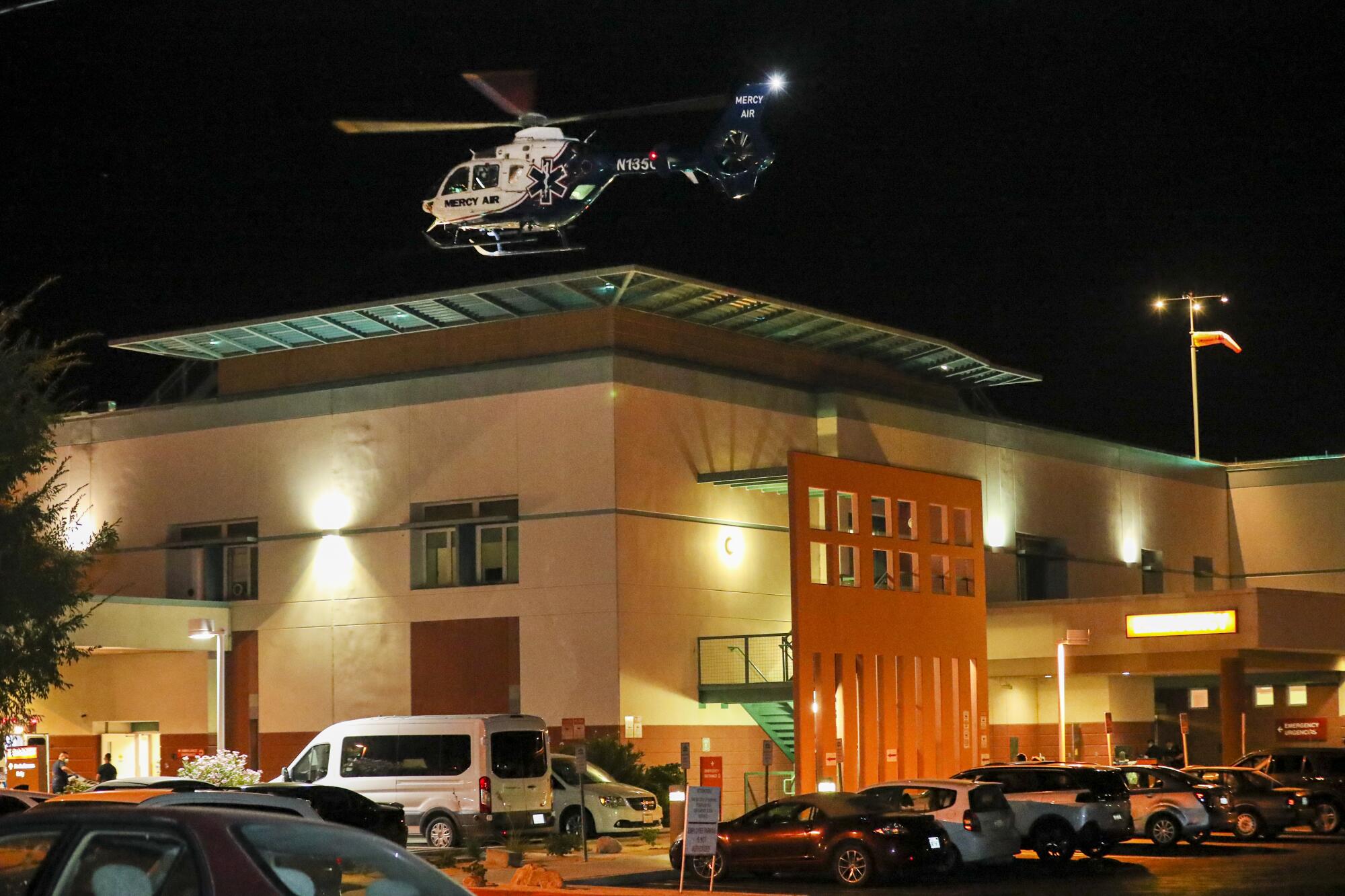
Bobeck said flights out of county average between four to five hours and in some cases up to six. He said the number of patient transports are lower than other bases in the surrounding area because of the long distance they have to fly.
“More than two [transports] is almost too much,” he said.
Hughes said that although Mercy Air workers wear protective suits and personal protective gear for each call, the long flights present an added risk because they are with the patients for a longer period of time. They said the high altitude poses a health risk for patients as well.
Before a transport request is accepted the crew has to weigh the risks. As a pilot, Bobeck looks at weather, distance and refueling points. Time, too. The FAA has strict rules about how long a pilot can work; the maximum is about 14 hours a day.

For the medic team, they have to take a patient’s medications and oxygen intake into account. COVID-19 patients, Hughes said, require a lot of oxygen.
So when the number of transports jumped in May, the team was working almost nonstop.
“I was flying almost every day,” Bobeck said.
The Sunday night call about the stroke patient was what the crew members were used to dealing with before the pandemic arrived. They didn’t require protection suits, and the round-trip flight would be about four hours total.
It was a little after 10 p.m. when the Mercy Air helicopter flew over the neighborhoods near El Centro Regional Medical Center. Its rotors sounded like a jackhammer in the distance as the chopper approached the facility.
At 10:04., the helicopter sat on the helipad. Bobeck took a walk around the aircraft, making sure everything was OK.
Inside, the medic team waited for paperwork and got the patient ready to go. By 10:32 p.m. the patient was aboard. Then helicopter lifted off and headed for UC San Diego Medical Center in Hillcrest.
It would be around 1 a.m. when the crew would return to the base. Each member, slowly walked back to their hotel rooms.
Another shift had ended. But the COVID-19 pandemic is surging, and there are surely many more flights ahead.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.











