Male doctors are disappearing from gynecology. Not everybody is thrilled about it

Some patients wait until Dr. Jerome Chelliah snaps on his gloves to make the request. Others blurt it out as soon as he walks in the exam room.
âIâd rather see a female doctor,â they say.
Chelliah thinks he can be a sensitive obstetrician-gynecologist even though heâs a man. But he has no choice but to comply.
âIâve been rejected many times over,â he said. âAs a person of color, I face discrimination in other ways, but itâs not so blatant.⌠People have no problem saying they donât want you.â
Chelliah is in a field of medicine where all the patients are female, and itâs more possible than ever for them to demand female doctors.
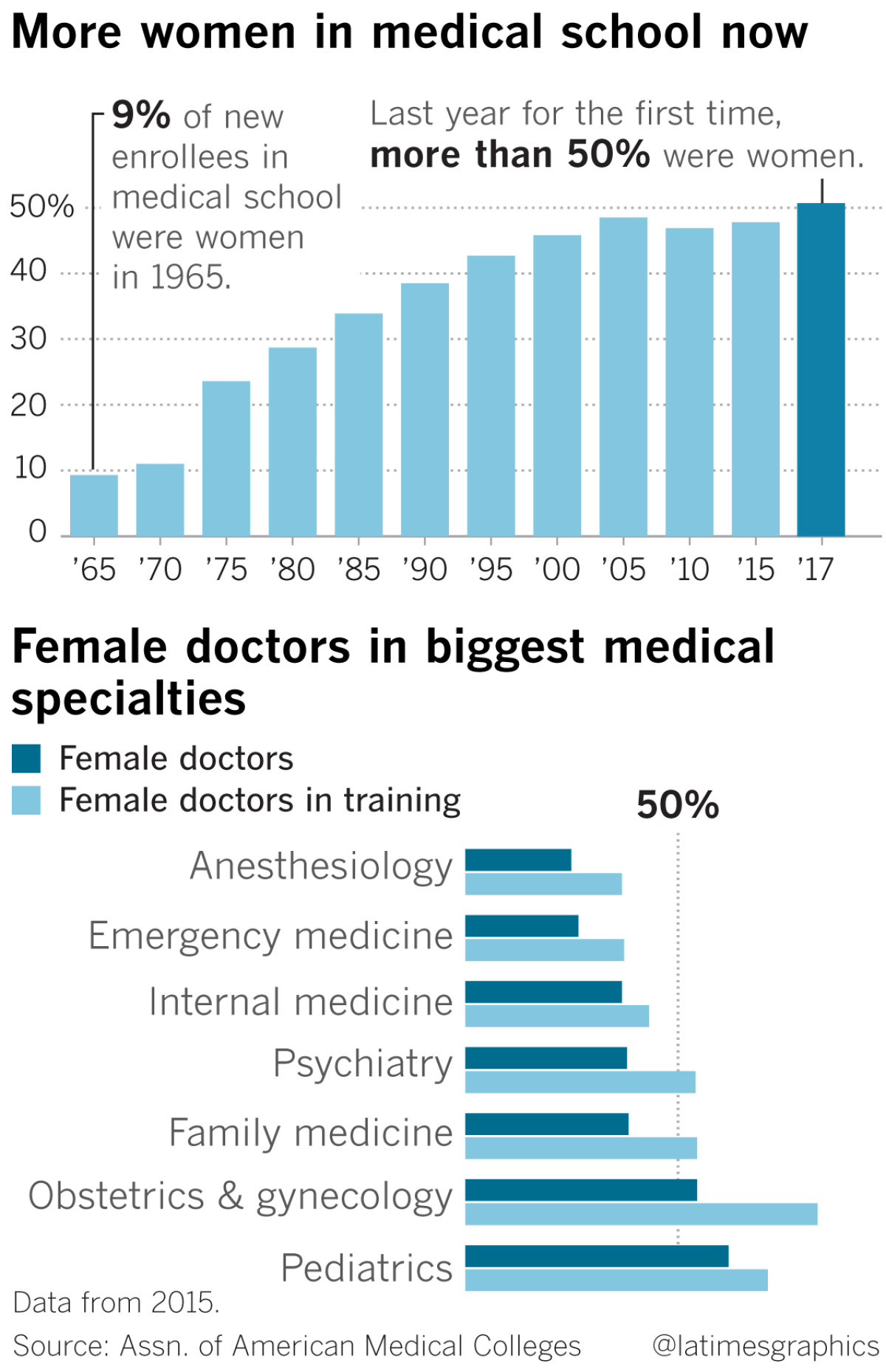
In 1970, 7% of gynecologists were women. Now 59% are.
Some men fear the falling number of male OB-GYNs could eventually lead to them being excluded from the specialty. They believe this is not only unfair, but also has subtle ramifications that go beyond patientsâ comfort on the examination table.
It's a perspective that garners little sympathy among women who had to fight for entrance into the male-dominated world of medicine.
âNobody was worried at all that there werenât enough women in OBâ in the 1970s, said Dr. Barbara Levy, an OB-GYN who trained then. âNobody paid any attention to us.â
The debate about male OB-GYNs taking place in universities and doctorsâ offices across the country has stoked concern and resentment among men and women, creating the ultimate collision of medicine and gender politics.
Chelliah, 28, became an OB-GYN because he wanted to get to know his patients, not just their medical problems.
OB-GYNs often treat the same women for decades, helping them pick a birth control method and cope with menopause. They care for mothers through pregnancy and share in the joy of new families.
âWe have a front-row seat to life that no one else has,â said Chelliah, who is completing OB-GYN residency training at Kaiser Permanente in Santa Clara, Calif.
Yet the job can feel cruel. Chelliah recently noticed a sign on a patient room with a picture of a babyâs foot. Above it, âFemale providers only.â He kept walking.
Patients can legally discriminate by sex, race or any other factor when choosing a physician, and some women feel more comfortable talking about intimate health topics with women.
Becoming an OB-GYN
- Four years of medical school, during which students try out different specialties, including OB-GYN
- Students who want to become OB-GYNs apply to residency training programs (76% of OB-GYN applicants were women last year)
- Four years of OB-GYN residency training
- OB-GYNs who want to subspecialize, such as in infertility, high-risk pregnancies or gynecological cancers, then do a three-year fellowship
Source: ACOG
Brooke Hamel, 19, recently went to get an intrauterine device inserted by a doctor recommended by her sister. She quickly started crying.
âHe touched me and I immediately lost it,â said Hamel, who lives in Yorktown, Va. âAs soon as I had to spread my legs, I was in a really vulnerable place, and I did not want to be in that position with a male.â
Male medical students say OB-GYN patients at universities often ask that they not be in the exam room. While female students are awed by helping deliver their first baby, men can miss out.
âIt sends a horrible message to men who might have a nascent interest in OB-GYN thatâs promptly quashed,â said Dr. Carl Smith, head of the OB-GYN department at the University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Men are now less likely than ever to try to become OB-GYNs. Only about 17% of current OB-GYN residents are men. Smith and others say that if their numbers keep dropping, it could weaken the field overall.
Dr. Reshma Jagsi, who studies gender issues in medicine at the University of Michigan, said a group of people with varied perspectives can better solve complex questions and make advances in a field. Men and women can offer important contributions to OB-GYN, she said.
âI really do believe that diversity improves the quality of care,â said Jagsi, who said gender isnât a factor when it comes to picking her own OB-GYN.
Dr. Saketh Guntupalli, a gynecological oncologist at the University of Colorado, raised the stakes. âIf you exclude 50% of people from anything, think about how much youâve lost,â he said. âYou might lose the next person who's going find a cure for cancer.â
These concerns appear to have given men pursuing OB-GYN an advantage. Medical school advisors told some that they wouldnât need to apply to as many residency programs as women with equivalent test scores, male students said.
If deciding between an equally qualified male and female candidate for a residency class that otherwise would have only women, program directors may favor the man, said Dr. Todd Jenkins, an OB-GYN at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
âWe find our faculty, our residents work better when we have a little mix,â he said.
Many women, patients and doctors alike, bristled at the idea that the field needs men.
In the 1970s, women struggled to get into medical school and to find doctors who wouldnât judge their sex lives, said Wendy Kline, a history of medicine professor at Purdue University. Activists viewed the male-run healthcare system as a gear of the patriarchy, she said.
Now 82% of residents training to be OB-GYNs are women. The proportion of female gynecologists in practice nationwide is expected to hit two-thirds by 2025. Gynecologists in TV and movies were once exclusively white men, but now the most well-known is arguably the Indian American character Dr. Mindy Lahiri of âThe Mindy Projectâ on TV.
Carol Weisman, a Penn State public health and OB-GYN professor, lauded womenâs success in the field and balked at efforts to recruit men. She pointed out that OB-GYN remains one of the hardest specialties to break into each year.

âIt seems to me that thereâs some residual sexism in that view, that we need men to be sure that weâre training the best possible people for our specialty. I find that very odd,â she said.
Outside of OB-GYN, fewer than a third of doctors are women. Women might dominate obstetrics and gynecology, but men dominate 37 of the 42 other medical specialties.
When Pari Ghodsi, an OB-GYN in Los Angeles, wears her scrubs outside the hospital, people ask, âAre you a nurse?â
âThat doesnât happen the other way around: If you see a man in scrubs, you assume heâs a doctor,â said Ghodsi, 36.
Nationally, thereâs no effort to draw more men to OB-GYN by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the OB-GYN professional organization, according to Levy, its vice president for health policy.
âThere are no right numbers or wrong numbers for what our specialty looks like,â she said.
Levy and others believe the shift is largely driven by patients seeking doctors who seem more like peers than white coats. Younger patients in particular say they can trust someone they know has been vulnerable in the same way.
âEven a female gynecologist has been to a gynecologist,â said Taylor Ortega, a 28-year-old comedian in New York City. âThereâs a lot we know about each other without knowing each other.â
Conchita Beronilla, 34, said she believed the male OB-GYN who cared for her while she was in labor couldnât understand her pain. She wanted to âsock him in the face,â she said.
âWe all go through cramps, we all go through menstrual cycles,â said Beronilla, who lives in San Francisco. âEven if they donât have kids, I believe women, we all go through the same particular suffering.â
These trends have influenced men too. Some feel socially excluded from OB-GYN departments in medical schools; they tend to be havens for women. Others say they donât want to perpetuate a history of men telling women what to do with their bodies.
Tanmaya Sambare, 24, signed up for a class called âMommies and Babiesâ in his first year at Stanford University medical school. But he started to think he wouldnât be able to sufficiently empathize with pregnant patients, he said.
âNo matter how hard I try I think itâs just capped ... because I donât have a uterus. Itâs not my fault, itâs not anyoneâs fault,â he said.
Some patients prefer male OB-GYNs â 8%, according to a recent review of 23 studies. Those women say theyâre gentler and better listeners and take their concerns more seriously, perhaps to overcome stereotypes.
Even more women â 41% in the same study â have no gender preference, a fact thatâs popular with doctors who say the desire for female physicians has been overstated.
âWe have to do a better job recruiting and dispelling some of the rumors and myths,â said Guntupalli, 39, of the University of Colorado. âFirst and foremost, women want a good doctor.â
Indeed, some female OB-GYNs said focusing on gender reduces womenâs skills to biology and doesnât account for transgender or gender-nonconforming patients who might not relate to female doctors simply because of the physicianâs gender.
âIâve never had kids, so what do I know about the pain of childbirth?â said Dr. Alison Jacoby, an OB-GYN who is part of UC San Franciscoâs Center of Excellence for Transgender Health. "It has everything to do with communication and empathy, and less on the gender of the provider.â
Daniel Spinosa, a medical student at UC San Diego, was told repeatedly that his gender wouldnât stop him from being a skilled OB-GYN.
Spinosa, 30, left a job on Wall Street because he wanted a career in which he could more tangibly help people. He thought he might want to be an oncologist.
âI wouldâve laughed you out of the room if youâd told me I was going to end up in OB-GYN,â Spinosa said.
But he said that while treating OB-GYN patients in medical school he learned he could develop meaningful relationships with them. He was almost never asked to leave patient rooms, because professors introduced him as âa member of our care teamâ instead of a âmale medical student.â
Older male OB-GYNs told him he could be happy with the career. OB-GYNs say they like that the field is dedicated to life, not death, and enjoy the unique mix of clinical work and surgery.
Spinosa, who will begin an OB-GYN training program this year, says he eventually wants to subspecialize in gynecological cancers. Male OB-GYNs are more likely to subspecialize, in large part because patients donât tend to be as picky about gender when they have a problem they need solved.
Spinosa, however, believes he could attract patients regardless. Itâs like his mentors told him, he said: âIf you provide good care, your patients will love you, and thatâs true in any field.â
Though female doctors cringed at the thought, some said they feared OB-GYN would lose prestige or pay if there were no men left in the field. Many believe that pediatricians, for example, are among the lowest-paid physicians because theyâre mostly women, so society takes their work less seriously.
âIf itâs not something men are doing, then itâs inherently less valuable,â Kline, of Purdue University, said.
Chelliah, who has two years left of OB-GYN training, said he wants to eventually go into healthcare administration, so he probably wonât treat patients daily. For now, though, he cherishes the patients who donât mind that heâs a man, he said.
âYou leave home knowing that what youâre good at and what youâre good for have aligned, and thatâs a beautiful moment,â he said.
Twitter: @skarlamangla




